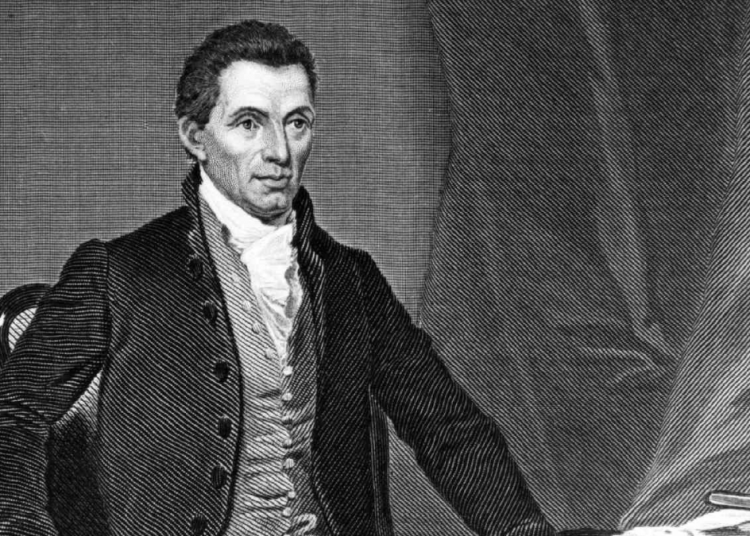
The Monroe Doctrine, proclaimed by President James Monroe on December 2, 1823, during his annual message to Congress, stands as a cornerstone of American foreign policy, emphasizing U.S. sovereignty and opposition to European interference in the Western Hemisphere.
Rooted in conservative principles of national independence and limited entanglement in foreign affairs, it declared that the United States would view any attempts by European powers to colonize or extend their political influence in the Americas as hostile acts.
This policy was crafted amid concerns over European monarchies, particularly after the Napoleonic Wars, seeking to restore colonial control in newly independent Latin American nations.



















Discussion about this post